I've seen countless customers walk into our shop, point confidently at two wheels, and guess which is cast and which is forged. They're usually wrong. The visual similarities make identification hard, even for professionals sometimes.
The main difference between cast and forged wheels is their manufacturing process. Cast wheels are made by pouring molten aluminum into molds, creating a granular internal structure. Forged wheels are made by applying extreme pressure to solid metal, creating a fibrous bamboo-like structure that's stronger and lighter.
](https://treewheels.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/image-1-cast-vs-forged-wheel-manufacturing-proces.png)
After years running Tree Wheels and specializing in high-end forged wheels, I've realized about 50% of individual buyers confuse these two wheel types. It's understandable - they look remarkably similar since both use aluminum alloys. But the differences become clear once you know what to look for.
How To Know If Wheels Are Cast Or Forged?
Many customers ask me this question after purchasing a vehicle with aftermarket wheels. Without documentation, it's hard to know what you're actually rolling on.
To identify if wheels are cast or forged, check the weight (forged are 20-30% lighter), look for machining marks (more precise on forged), examine spoke thickness (forged can be thinner), and consider the price (forged cost significantly more). The manufacturer's documentation is the most reliable confirmation.
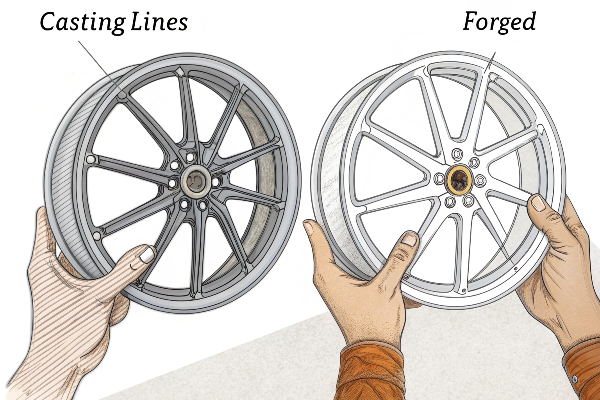
The internal structure of these wheels tells the real story about their performance differences. Cast wheels have a granular internal structure, like sand packed together. This happens because as molten aluminum cools in the mold, it forms small crystalline structures. In contrast, forged wheels have a fibrous structure similar to bamboo. The intense pressure during forging aligns the metal's grain in one direction, creating that fibrous pattern.
| Identification Factor | Cast Wheels | Forged Wheels |
|---|---|---|
| Internal Structure | Granular, like packed sand | Fibrous, similar to bamboo |
| Weight | Standard weight | 20-30% lighter than cast |
| Failure Pattern | Typically crack completely | Usually bend without breaking |
| Manufacturing Marks | Casting lines where molds joined | Precision machining marks |
| Spoke Design | Thicker, more uniform | Can be thinner, more complex |
| Price Range | More affordable | 3-4 times more expensive |
Weight difference is one of the easiest ways to tell them apart. When customers visit our showroom, I often let them hold comparable designs in cast versus forged versions. The forged wheel is noticeably lighter - typically 20-30% less weight for the same size and design. This weight saving might seem small, but it significantly improves vehicle performance through reduced unsprung weight.
For serious enthusiasts or professionals who want to be absolutely certain, examining the manufacturing marks can provide clues. Cast wheels typically have casting lines where the mold sections joined, while forged wheels often show machining marks from the milling process used to create their designs.
How To Tell The Difference Between Cast And Forged?
I've had customers bring in wheels they couldn't identify. Without proper markings, distinguishing between high-quality cast and forged wheels challenges even experienced professionals.
To differentiate between cast and forged wheels, examine the back of the spokes - forged wheels typically have more complex, sculptured designs with thinner cross-sections. Cast wheels usually have thicker, more uniform spokes with visible casting marks. The price tag also helps - forged wheels generally cost 3-4 times more.
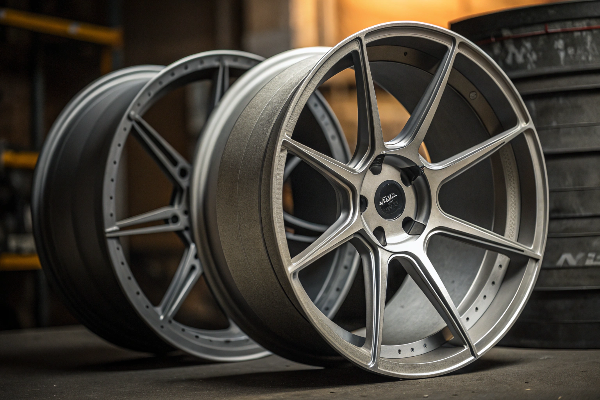

Since founding Tree Wheels, I've realized that visual inspection alone isn't always reliable for telling wheel types apart. The manufacturing processes have become so advanced that premium cast wheels can look remarkably similar to forged options. That's why I typically look at multiple factors before making a determination.
| Identification Method | What to Look For |
|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Forged: More intricate designs, sharper edges, deeper pockets Cast: More uniform thickness, possible casting marks |
| Weight Test | Forged: Noticeably lighter (20-30% less) than comparable cast design |
| Sound Test | Forged: Higher, clearer ring when gently tapped Cast: Duller sound when tapped |
| Weight Distribution | Forged: More balanced across the wheel Cast: May have slight inconsistencies |
| Manufacturer Markings | Look for stamps/engravings indicating "forged" or specific alloy types |
The finishing process provides some clues. Forged wheels often feature more intricate designs with sharper edges and deeper pockets. This is possible because the forged aluminum's strength allows for thinner cross-sections without compromising structural integrity. When I examine the backside of wheel spokes, cast versions typically have a more uniform thickness and sometimes show telltale signs of the casting process.
Weight distribution is another factor I consider. Forged wheels generally have more balanced weight distributionw.youtube.com/watch?v=KjgyrEo5GcU) distribution due to their production process. In our testing facility, we've observed that cast wheels often have slight weight inconsistencies across different sections of the same wheel. This isn't visible to the eye but becomes apparent during precision balancing.
Which Is Better, Cast Or Forged Wheels?
Customers frequently ask me this question, often expecting a simple answer. The honest truth is more nuanced than most realize.
Forged wheels are technically superior with their lighter weight, greater strength, and better performance characteristics. However, cast wheels are completely sufficient for everyday commuter vehicles and cost significantly less. The "better" choice depends entirely on your vehicle, driving style, and budget.

Through my years manufacturing high-end wheels, I've developed a practical perspective on this question. While we specialize in premium forged wheels at Tree Wheels, I always give honest recommendations based on customer needs. The price difference is substantial - forged wheels can cost 3-4 times more than comparable cast designs.
| Performance Factor | Cast Wheels | Forged Wheels | Real-world Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | Standard | 20-30% lighter | Better acceleration, braking, and fuel efficiency |
| Strength | Good | Superior | Better durability, especially for performance driving |
| Impact Resistance | May crack under severe impact | More likely to bend than break | Higher safety margin |
| Heat Dissipation | Good | Excellent | Better brake performance during intense driving |
| Cost | More affordable | 3-4x more expensive | Significant price premium |
| Best Use Case | Daily commuter vehicles | Performance cars, track use | Different ideal applications |
For performance metrics, forged wheels clearly outperform cast options in several key areas. First, they're significantly lighter, which reduces unsprung weight - the mass that your suspension must control. This translates to more responsive handling, better acceleration, and improved braking performance. A vehicle equipped with forged wheels can actually stop several feet shorter from high speeds compared to the same vehicle with cast wheels.
Strength testing reveals dramatic differences as well. In our laboratory impact tests, forged wheels can withstand much greater forces before deforming. This matters particularly for performance driving or when encountering road hazards like potholes. The forging process aligns the aluminum's grain structure, similar to how bamboo gains strength from its fibrous makeup.
But these advantages primarily matter for specific usage scenarios. If you drive a standard commuter car at normal speeds, cast wheels will serve you perfectly well for years. The performance benefits of forged wheels become truly meaningful for sports cars, track use, or driving enthusiasts who push their vehicles to the limits.
How Do I Tell What Material My Wheels Are?
This question comes up frequently from buyers of used vehicles or those inheriting wheels without documentation. Identifying material composition isn't always straightforward.
To determine wheel material, check for markings indicating "forged aluminum" or specific alloy types like 6061-T6. Magnet tests help identify steel wheels (magnetic) versus aluminum (non-magnetic). Weight provides clues too - aluminum wheels are significantly lighter than steel, and forged aluminum weighs less than cast.
In our wheel manufacturing facility, material selection is one of the most critical decisions we make. Different alloys offer varying benefits in terms of strength, weight, and machinability. For our forged wheels, we typically use premium 6061-T6 or 7075-T6 aluminum alloys, while cast wheels often use A356 or similar alloys.
| Wheel Material | Identification Methods | Typical Characteristics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Magnetic, heavier, simpler design | Durable, heavier, prone to rust | Economy cars, winter wheels |
| Cast Aluminum | Non-magnetic, complex designs possible | Medium weight, good strength | Most standard vehicles |
| Forged Aluminum | Non-magnetic, lightest weight, intricate designs | Premium strength-to-weight ratio | Performance vehicles |
| Carbon Fiber | Very lightweight, distinctive weave pattern | Extremely light, limited designs | High-end sports cars, racing |
| Magnesium | Very lightweight, often racing-specific | Lightest metal wheels, expensive | Racing applications |
The material directly impacts how the wheel performs and ages over time. I've seen numerous examples of different wheel materials after years of service. Steel wheels, still common on many economy vehicles, typically show surface rust but maintain structural integrity for decades. Cast aluminum wheels might develop small cracks near lug holes after extensive use, especially in harsh conditions. Quality forged wheels often look almost new structurally even after years of hard use.
When helping customers identify their wheel material, I start with visual inspection. Steel wheels are typically heavier, simpler in design, and often painted black or silver. They're sometimes covered with hubcaps. Aluminum wheels (both cast and forged) allow for more complex designs and come in various finishes including machined, painted, and polished appearances.
The magnet test is reliable for distinguishing steel from aluminum, as steel is magnetic while aluminum isn't. However, this doesn't help differentiate between cast and forged aluminum wheels. For that distinction, weight provides useful clues - forged aluminum wheels typically weigh 20-30% less than comparable cast designs.
Conclusion
Understanding wheel types helps you make informed decisions that match your driving needs and budget. For everyday driving, quality cast wheels work perfectly fine, while performance enthusiasts truly benefit from forged options.
Tree Wheels crafts premium forged wheels that deliver exceptional performance, but we'll always recommend what truly fits your specific needs rather than just our highest-margin products.



